HTML Area Tag
The <area> tag is an HTML tag used inside an image map. An image map is a single image that has multiple clickable areas — each area can take the user to a different link or perform a different action. So instead of placing separate links all around an image, you can define clickable hotspots using the <area> tag.
The <area> tag does not work by itself. It always needs to be used inside a <map> element, and the <map> is connected to an image using the usemap attribute. Think of a world map where you click on different countries, and each click takes you to a different page — that’s an image map, and it uses <area> tags.
Syntax -
<area>…</area>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| alt | Text Specifies alternative text when image is not available. Required if the href attribute is present. |
| coords | Specifies pixel coordinates of the area and its shape. For rectangular: comma-separated list of four values for left, top, right and bottom. For circular: comma-separated list of three values for left, top and radius. For polygonal: comma-separated list containing an even number of values, specifying the left and top of each point of the shape |
| download | Specifies the target should be downloaded instead of navigated to. |
| href | URL. Specifies the destination the area. |
| hreflang | Language code Specifies the language of the target link. This attribute can be used if href is used |
| Media | media_query Specifies media/device the linked document is optimized |
| Nohref | Value Specifies area has no associated link. |
| rel | Specifies the relationship between the link’s page and the link’s target destination. alternate: Indicates an alternative version of the current web page. author: Indicates author of the page / article. bookmark: link to the current section of the page. help: Indicates the Help specific to the context. license: Indicates copyright license for the current document. next: Indicates the linked next page in the sequence. nofollow: Indicates the linked resource is not certified by the current document’s author. noreferrer: Indicates the browser not to send an HTTP referrer header. prefetch: Indicates the linked resource should be cached. prev: Indicates the linked previous page in the sequence. search: Indicates the search facility used to search the current, and related, documents. tag: A tagging term that applies to the link. |
| shape | Specifies the area’s shape. rect: Rectangle. This is the default value. Circle: circle poly: Polygon. default: The area becomes the full image area. |
| target | Specifies in which the target destination should open. _self: Opens link in current window / tab. |
| type | Text. Specifies type of the linked resource. |
Example -
Scenario - A simple example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> area example</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="world-map.png" usemap="#worldmap"
width="500" height="300" alt="Clickable world map">
<map name="worldmap">
<area shape="rect" coords="50,50,150,150"
href="usa.htm" alt="USA" title="Go to USA page">
<area shape="circle" coords="335,150,25"
href="india.htm" alt="India" title="Go to India page">
</map>
</body>
</html>
Output -
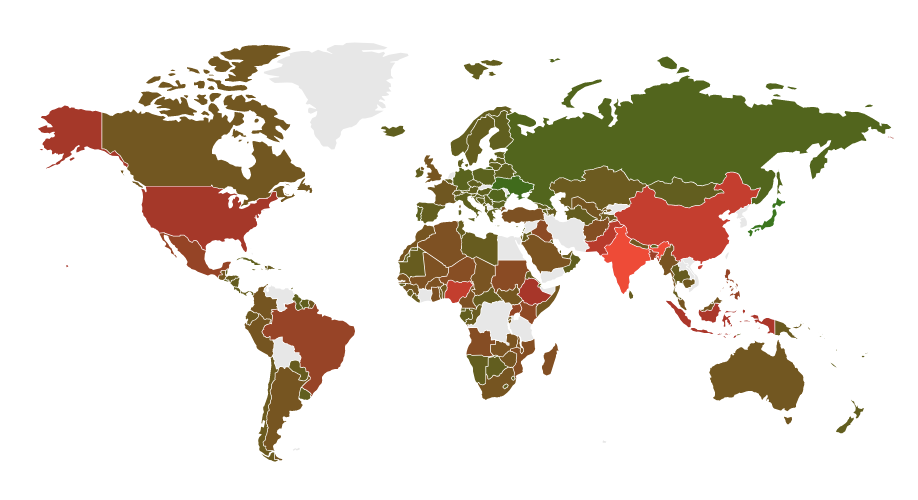
Move the cursor to USA and India maps to see the text and click on it to navigate to the respective pages.
Explaining Example -
The image shows a world map. Two areas are defined: one rectangle (USA), and one circle (India). When the user clicks on those parts of the image, they go to different pages. Tooltips appear when hovering, thanks to the title attribute.
