Agile QA Role In Scrum
QA in Scrum
In traditional software development, QA often comes into play after the development phase is complete. However, in Scrum, QA is integrated throughout the development process. This means QA professionals work alongside developers from the beginning, ensuring quality is built into the product from the start. By being involved early, QA can identify potential issues sooner, leading to more efficient and effective development cycles. This collaborative approach helps in delivering a high-quality product that meets customer expectations.
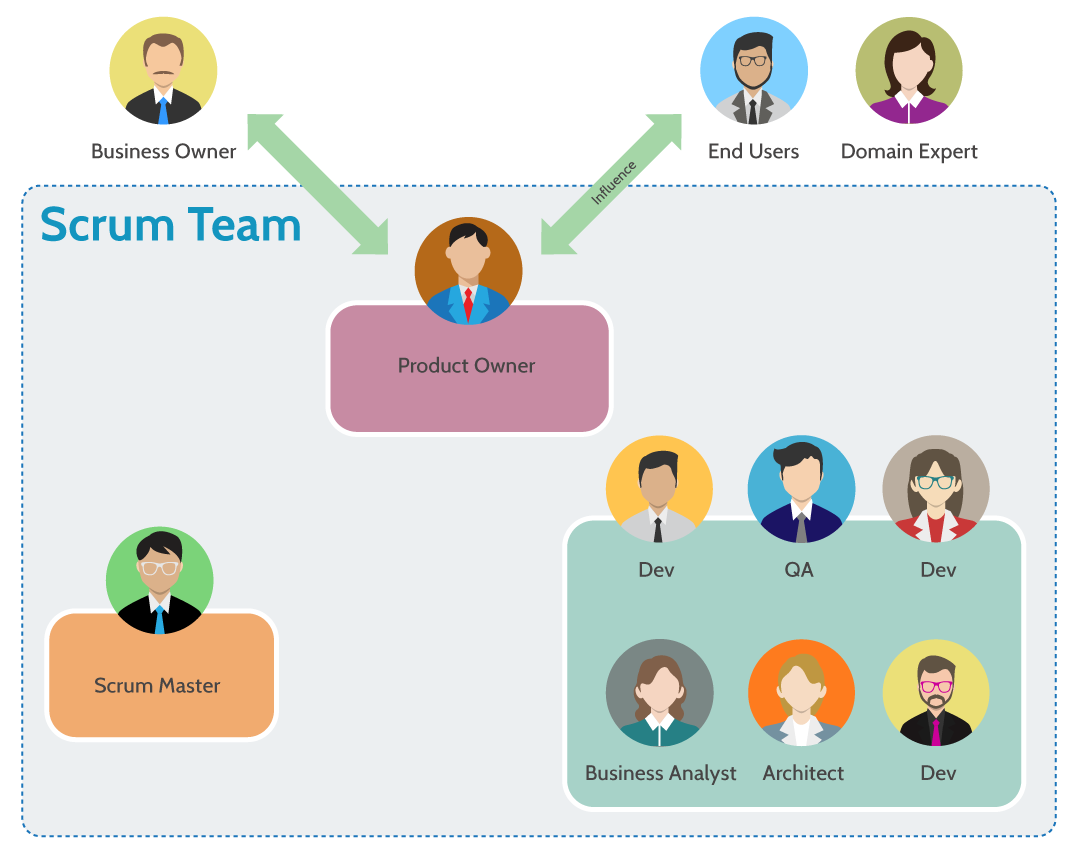
Responsibilities of QA in Scrum
QA professionals in Scrum have several key responsibilities:
- Test Planning: They help in planning tests for each sprint, ensuring that all features are testable and meet the acceptance criteria.
- Test Execution: QA executes various tests, including functional, regression, and performance tests, to validate the product's quality.
- Bug Reporting: When issues are found, QA reports them promptly, facilitating quick fixes and maintaining the development flow.
- Continuous Feedback: QA provides ongoing feedback to the team, contributing to continuous improvement and adaptation.
Skills Required for QA in Scrum
To be effective in a Scrum environment, QA professionals should possess certain skills:
- Communication: Strong communication skills are essential for collaborating with team members and stakeholders.
- Automation Testing: Knowledge of automation tools helps in executing repetitive tests efficiently, saving time and resources.
- Understanding of Agile Principles: Familiarity with Agile methodologies ensures that QA aligns with the team's workflow and goals.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze requirements and identify potential issues is crucial for proactive quality assurance.
Collaboration with the Scrum Team
In Scrum, QA is not a separate entity but an integral part of the development team. This collaboration involves:
- Daily Stand-ups: QA participates in daily meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and coordinate with developers.
- Sprint Planning: QA contributes to planning sessions, ensuring that testing considerations are included in the sprint goals.
- Retrospectives: QA engages in retrospectives to reflect on the sprint and suggest improvements for future iterations.
- Shared Responsibility: Quality is a collective responsibility; QA works closely with developers to maintain high standards.
Role of the Tester in Review and Retrospective meetings
The Scrum framework emphasizes continuous improvement, and QA plays a vital role in this process:
- Feedback Loops: QA provides regular feedback on product quality, helping the team make informed decisions.
- Process Enhancement: By analyzing testing outcomes, QA suggests process improvements to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- Learning and Development: QA professionals continuously update their skills to adapt to new tools and methodologies.
- Customer Satisfaction: Through diligent testing and collaboration, QA ensures that the final product meets or exceeds customer expectations.
