Agile Scrum Overview
What is Scrum?
Scrum is a framework within Agile methodology that helps teams work together to develop, deliver, and sustain complex products. It emphasizes collaboration, accountability, and iterative progress toward a well-defined goal. The core idea is to break down large projects into manageable chunks called "Sprints," allowing teams to adapt to changes quickly and efficiently.
Scrum Team Structure
A Scrum Team is cross-functional, meaning it includes all the expertise necessary to deliver the product increment. The team typically comprises:
- Product Owner: Responsible for maximizing the value of the product and managing the Product Backlog.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, helps remove impediments, and ensures that Scrum practices are followed.
- Development Team: Professionals who work together to deliver a potentially releasable Increment of "Done" product at the end of each Sprint.
Scrum Events (Ceremonies)
Scrum defines four formal events for inspection and adaptation:
- Sprint Planning: Determines what can be delivered in the Increment resulting from the upcoming Sprint and how the work needed to deliver the Increment will be achieved.
- Daily Scrum: A 15-minute time-boxed event for the Development Team to synchronize activities and create a plan for the next 24 hours.
- Sprint Review: Held at the end of the Sprint to inspect the Increment and adapt the Product Backlog if needed.
- Sprint Retrospective: An opportunity for the Scrum Team to inspect itself and create a plan for improvements to be enacted during the next Sprint.
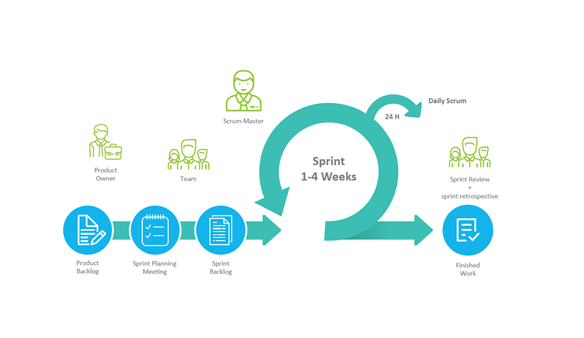
Scrum Workflow
The Scrum process is iterative and incremental, promoting frequent inspection and adaptation. A typical workflow includes:
- Product Backlog Creation: The Product Owner creates and maintains a prioritized list of features, enhancements, and fixes.
- Sprint Planning: The team selects items from the Product Backlog to work on during the Sprint.
- Sprint Execution: The Development Team works on the selected items, holding Daily Scrums to coordinate efforts.
- Sprint Review: The team presents the completed work to stakeholders for feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: The team reflects on the Sprint to identify improvements for the next iteration.
This cycle repeats, allowing for continuous delivery of valuable product increments.
