Hadoop Architecture
Hadoop is an open-source framework that is distributed, scalable, capable of batch processing, and designed for fault tolerance. It can store and process vast amounts of data, commonly referred to as Big Data. Hadoop efficiently stores large volumes of data across a cluster of commodity hardware.
In addition to serving as a storage system, Hadoop also functions as a platform for processing large datasets. There are primarily five key components within this runtime environment, arranged from top to bottom -

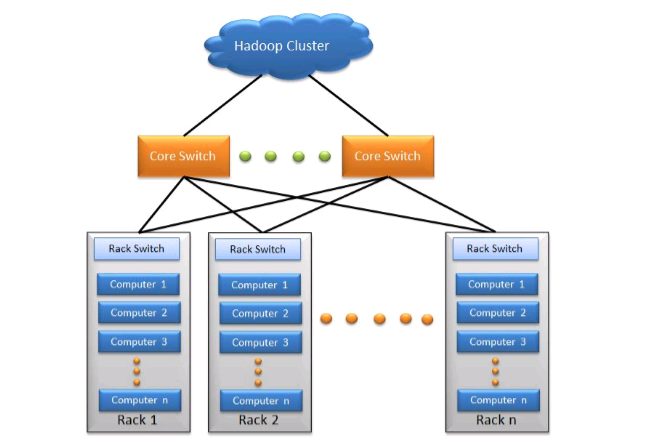
1. Cluster -
A Hadoop cluster is specifically designed for storing and analyzing large amounts of unstructured data in a distributed computing environment. A cluster consists of nodes, which are also known as host machines, forming the hardware component of the infrastructure.
These clusters are often referred to as "shared nothing" systems because the only resource shared among the nodes is the network that connects them. Hadoop clusters are well-known for significantly increasing the speed of data analysis applications.
Hadoop clusters are highly scalable: If a cluster's processing data growing by volumes, new additional cluster nodes can be added to increase throughput. Hadoop clusters are highly resistant to failure because the data always copied onto multiple cluster nodes, which ensures that the data is not lost if one node fails. This is the hardware part of the infrastructure.
2. YARN Infrastructure -
YARN is abbreviated as Yet Another Resource Negotiator. Apache Yarn is a part or outside of Hadoop that can act as a standalone resource manager.
It is the framework responsible for providing the computational resources needed for application executions. Yarn consists of two important elements are: Resource Manager and Node Manager.
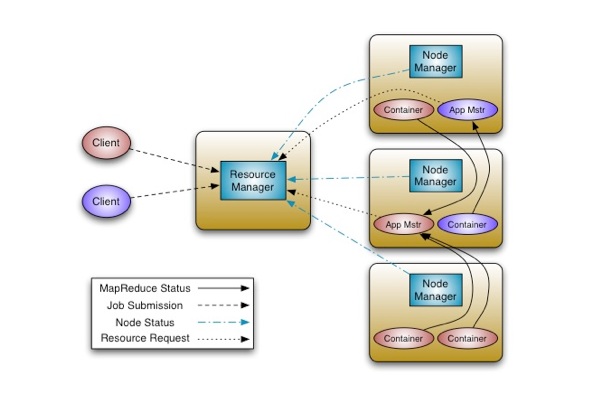
Resource Manager -
Resource manager runs several services and has the information where the slaves are located and how many resources they have. One resource manager can be assigned to one cluster per the master.
The most important service among them is the Resource Scheduler that decides how to assign the resources. The Resource Manager does this job with the Scheduler and Applications Manager.
Node Manager -
Node Manager takes instructions from the Yarn scheduler to decide which node should run which task. The Node Manager reports CPU, memory, disk and network usage to the Resource Manager to decide where to direct new tasks.
Node Manager is the slave of the infrastructure. It sends a heartbeat to the Resource Manager periodically. More than one Node Managers can be assigned to one Cluster.
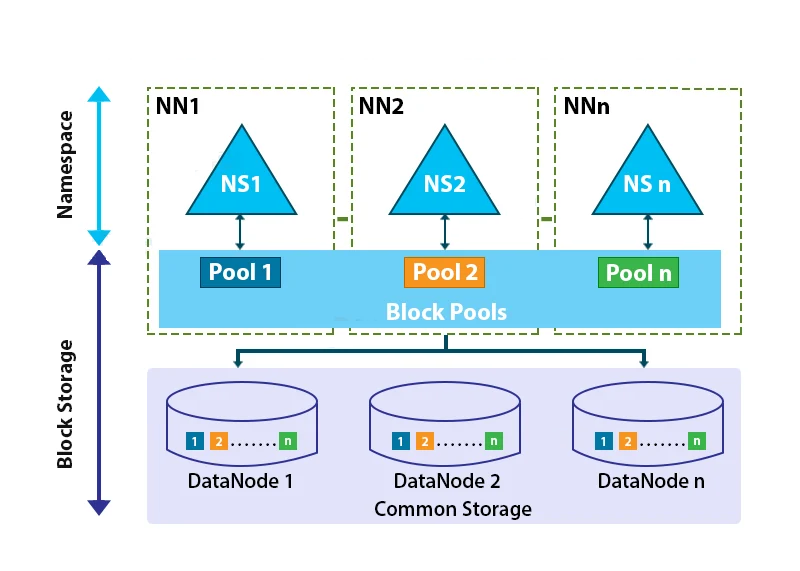
3. HDFS Federation -
HDFS federation is a framework designed to provide permanent, reliable, and distributed storage. It is typically used for storing inputs and outputs, but not intermediate data. This framework supports multiple namespaces within the cluster, enhancing scalability and isolation.
To achieve horizontal scaling of the name service, federation employs multiple independent name nodes and namespaces. These name nodes operate independently and do not require coordination with one another. All name nodes share the same data nodes, which serve as common storage for data blocks.
Each data node registers with every name node in the cluster. Data nodes periodically send heartbeats and respond to commands from the name nodes.
4. Storage Solutions -
Hadoop utilizes various storage solutions for data storage and processing, which will be discussed in subsequent chapters.
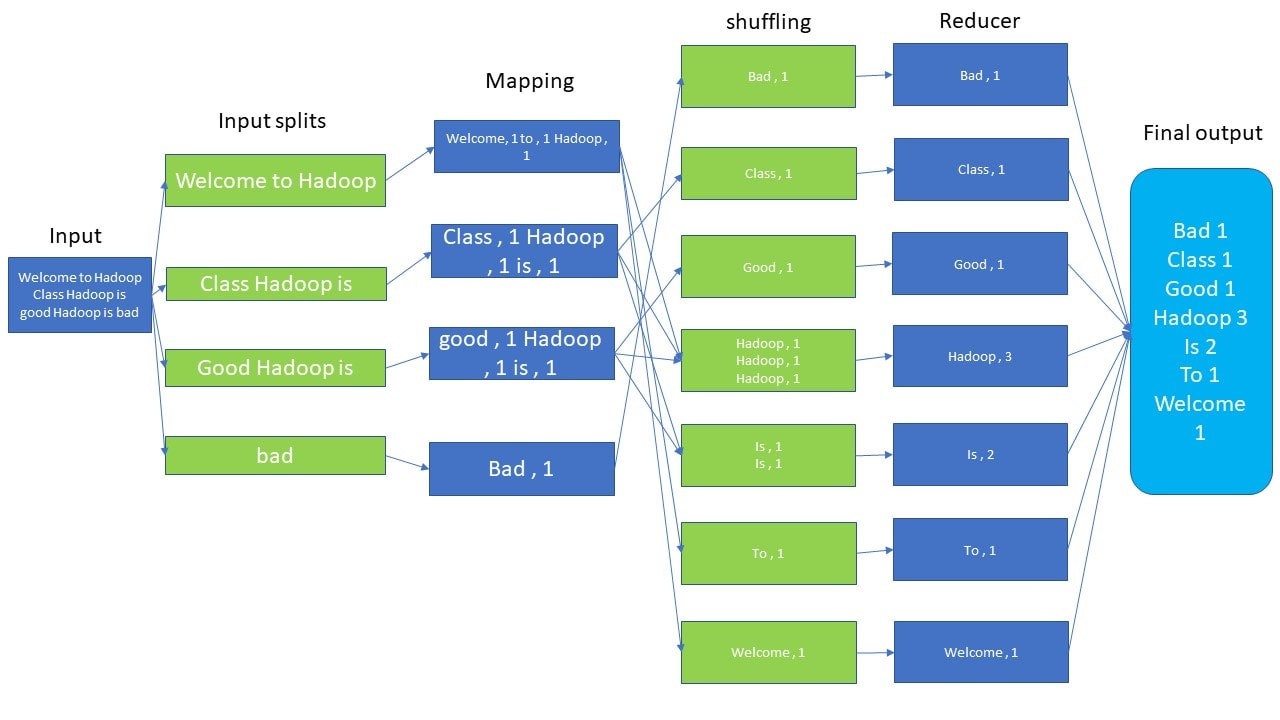
5. MapReduce Framework -
The MapReduce framework is the software layer that implements the MapReduce paradigm. Processing can occur on data stored in either a filesystem (unstructured data) or a database (structured data). A MapReduce framework typically consists of three steps -
- Map: Each node applies the map function to its local data and writes the output to temporary storage. A master node ensures that only one copy of any redundant input data is processed.
- Shuffle: Each node redistributes data based on the output keys, ensuring that all data associated with a particular key is located on the same node.
- Reduce: Each node processes each group of output data according to its key in parallel.
The YARN infrastructure and the HDFS federation are completely decoupled and independent. YARN provides the resources necessary for running applications, while the HDFS federation offers storage. The MapReduce framework is the only framework that operates on top of YARN.
