Hadoop Scheduling
Earlier to Hadoop 2, Hadoop MapReduce is a software framework for writing applications that process huge amounts of data (terabytes to petabytes) in-parallel on the large Hadoop cluster. This framework is responsible for scheduling tasks, monitoring them, and re-executes the failed task.
In Hadoop 2, a Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN) was introduced. The fundamental idea behind the YARN introduction is to distribute the functionalities of resource management and job scheduling or monitoring into distinct daemons that are Resource Manager, Application Master, and Node Manager.
Resource Manager is the master daemon that settles resources among all the applications in the system. Node Manager is the slave daemon accountable for containers, monitoring their resource usage, and reporting the same to Resource Manager or Schedulers. Application Master negotiates resources from the Resource Manager and works with the Node Manager to execute and monitor the task.
The Resource Manager consists of two major components: the Scheduler and the Application Manager. Schedulers in YARN Resource Manager is a pure scheduler that is responsible for allotting resources to different running applications. It is not responsible for monitoring or tracking the status of an application. Therefore, the scheduler does not guarantee about restarting the tasks that are failed either due to hardware failure or application failure.
Below are three types of schedulers used to schedule the jobs -
- FIFO Scheduler
- Fair Scheduler
- Capacity Scheduler
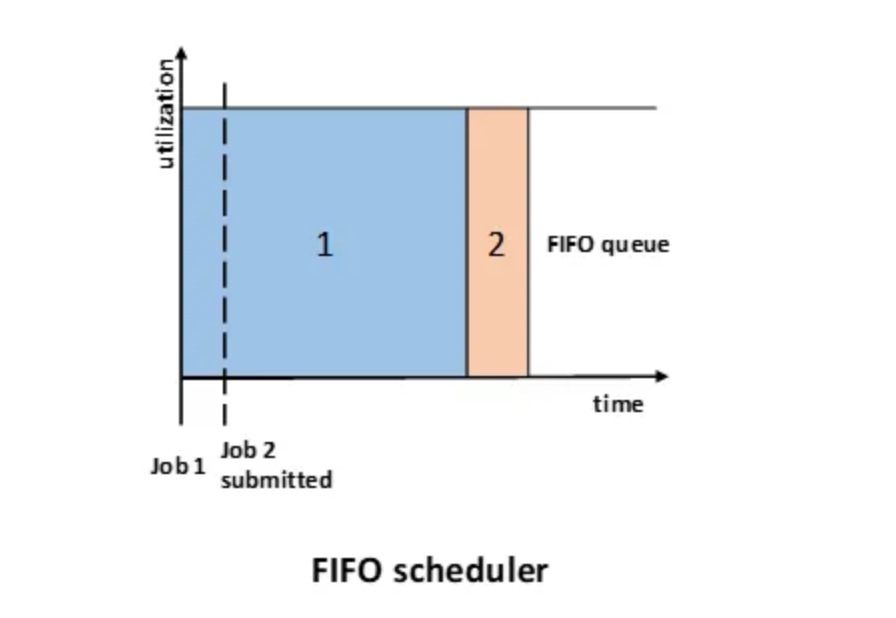
FIFO Scheduler -
The FIFO Scheduler prioritizes applications based on the order in which they are submitted. Applications are placed in a queue and executed according to their submission time—those submitted first are processed first.
In this system, the size and priority of the applications do not affect their order in the queue. Only after the first application request is fully satisfied will the next application in the queue be served.

Advantages -
- It is easy to understand and requires no configuration.
- Jobs are executed in the order they are submitted.
Disadvantages -
- This setup is not suitable for shared clusters. If a large application is scheduled before a shorter one, it will consume all the resources in the cluster, forcing the shorter application to wait for its turn. This situation can lead to resource starvation.
- It does not consider the balance of resource allocation between long and short applications.
Capacity Scheduler -
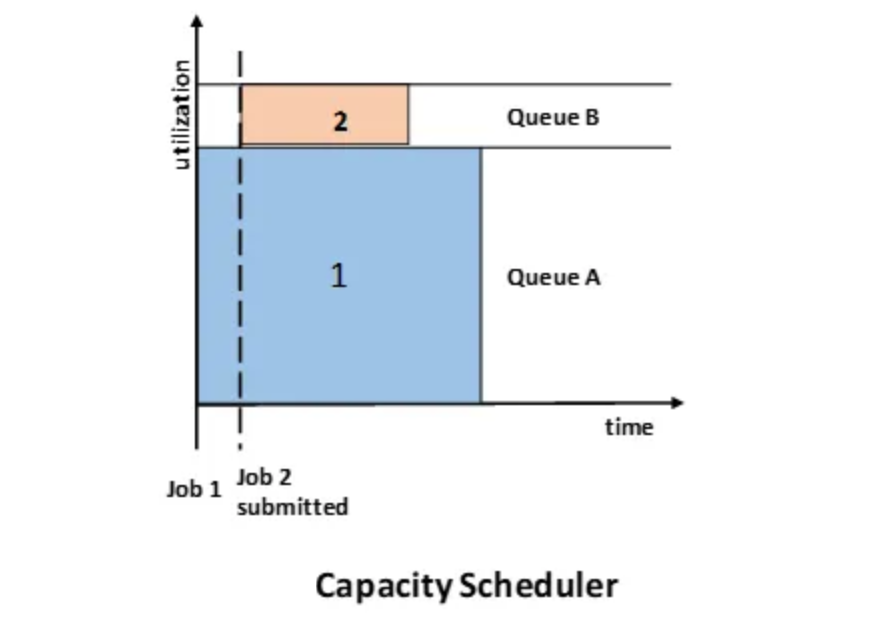
The Capacity Scheduler was developed by Yahoo. Capacity Scheduler is like Fair Scheduler with some differences. It distributes jobs fairly among users and is specifically designed for large clusters.
In capacity scheduling, multiple queues are created, each with a configurable number of map and reduce slots. Each queue is assigned a guaranteed capacity.
All queues are monitored to ensure they use their allocated capacity. If a queue is not utilizing its full capacity, the excess can be temporarily reallocated to other queues. In capacity scheduling, higher-priority jobs are given access to resources before lower-priority jobs.
In capacity scheduling, strict access controls are implemented on queues. These controls are defined for each queue and restrict the ability to submit, view, and modify jobs within them.
Advantages -
- Ideal for managing multiple clients or priority tasks in a Hadoop cluster
- It ensures maximum throughput within the system.
Disadvantages -
- More complex.
- Not easy to configure for everyone
Fair Scheduler -
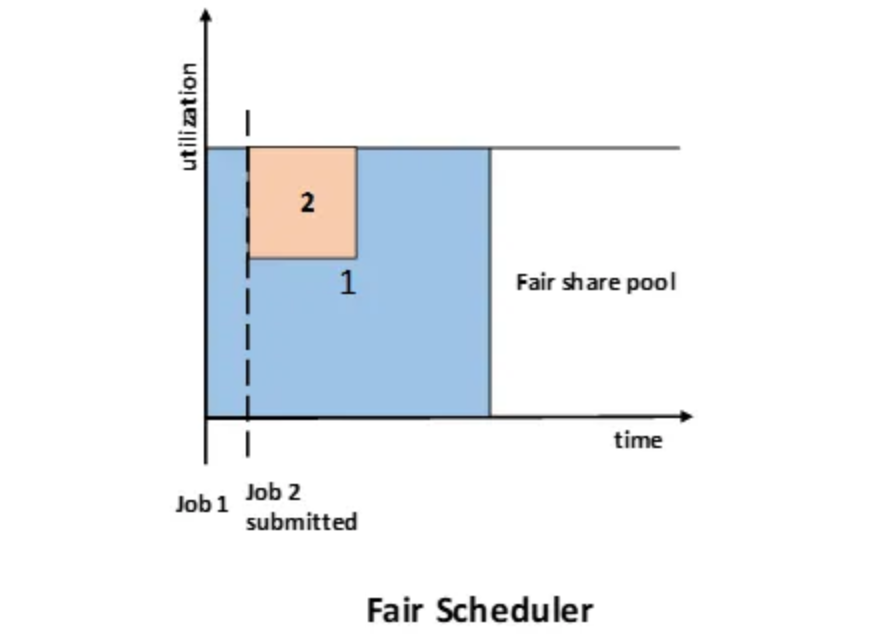
The fair scheduler was developed by Facebook. This scheduler is designed to allocate resources to jobs based on their average completion time. As a result, jobs that require less time to complete can access the CPU alongside jobs that take longer to execute.
The Hadoop implementation creates a series of pools where jobs are assigned for selection by the scheduler. Each pool can be allocated a specific number of shares to manage resource distribution among the jobs within that pool. By default, all pools have equal shares; however, it is possible to customize the configuration to assign more or fewer shares based on the job type.
Each user is assigned to a single pool to ensure fairness. Over time, every user receives their fair share of the cluster's capacity. A user only gets access to their assigned share of resources, regardless of the number of jobs they submit. If a particular user does not submit any jobs, their resources will remain unused and will not be shared with others.
Multiple users can run jobs on the cluster at the same time.
Advantages -
- Resources allocated to each application are based on its priority.
- It can restrict the number of concurrent tasks in a specific pool or queue.
Disadvantages -
- The configuration is required.
