Hadoop Eco-systems
Hadoop Ecosystem is neither a programming language nor a service. It is a platform or framework designed to solve big data problems. Hadoop is best known for its MapReduce capabilities and its distributed file system, HDFS (previously known as NDFS).
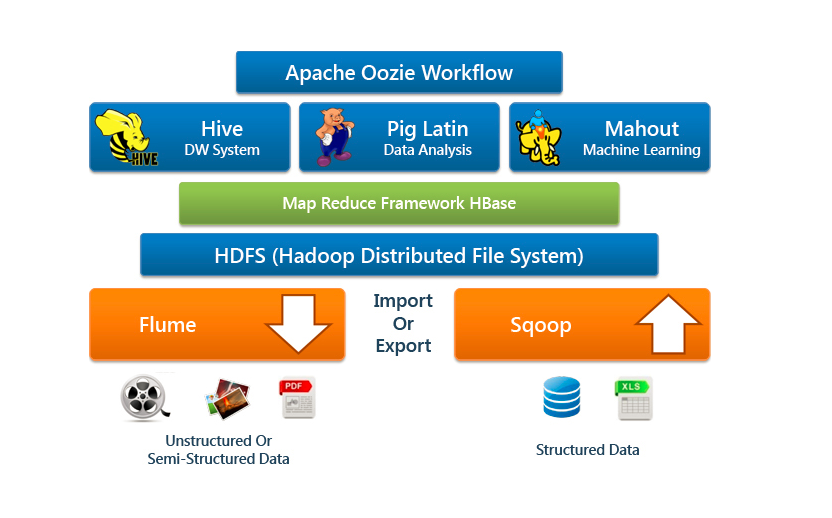
HDFS -
HDFS abbreviated as Hadoop distributed file system and is the core component of Hadoop Ecosystem. HDFS is a distributed file system and serves as the primary storage system for Hadoop, distributing data across multiple systems. It enables the storage of various types of large data sets, including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
Hadoop interact directly with HDFS by shell-like commands. HDFS has two core components, i.e. Name Node and Data Node. In HDFS, Name Node stores metadata and Data Node stores the actual data.
MapReduce -
MapReduce is the programming model used in Hadoop. It is a software framework designed to help developers write applications for processing large data sets. MapReduce programs execute parallel algorithms within the distributed Hadoop environment.
The MapReduce component consists of two phases: the Map phase and the Reduce phase. Each of these phases takes key-value pairs as input and produces key-value pairs as output. In addition to the built-in functions, programmers can also define two specific functions: the map function and the reduce function.
Hadoop streaming -
Hadoop Streaming is a utility used by developers who are unable to write MapReduce code in other programming languages. It is a generic API that allows Mappers and Reducers to be written in any language, such as C, Perl, Python, C++, etc. These Mappers and Reducers receive their input and output through standard input (stdin) and standard output (stdout) as (key, value) pairs. Hadoop Streaming is particularly well-suited for text processing.
Hive -
Apache Hive is an open-source system designed for querying and analyzing large datasets stored within Hadoop files. It facilitates reading, writing, and managing extensive data sets in a distributed environment using a SQL-like interface. Hive utilizes a language known as Hive Query Language (HQL), which resembles SQL.
HiveQL automatically converts SQL-like queries into MapReduce jobs that run on Hadoop. Users can execute HQL commands through the Hive Command Line Interface (CLI). The main components of Hive include:
- Megastore – Stores metadata.
- Driver – Manages the lifecycle of a HiveQL statement.
- Query compiler – Compiles HiveQL into a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
- Hive server – Provides a Thrift interface and JDBC/ODBC server for connectivity.
Pig -
Apache Pig is a high-level platform designed for analyzing and querying large datasets stored in HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System). It consists of two main components: Pig Latin and the Pig Runtime. Pig Latin is the language used for data manipulation, while the Pig Runtime serves as the execution environment.
To run Pig, a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is required. Apache Pig offers impressive price-performance ratios and ensures high availability for data processing tasks.
Sqoop -
Sqoop is a tool that imports data from external sources into various components of the Hadoop ecosystem, such as HDFS, HBase, or Hive. It can also export data from Hadoop back to external sources.
Sqoop is compatible with several relational databases, including Teradata, Netezza, Oracle, and MySQL. Its features include the ability to write directly to ORC files, efficient data analysis, fast data copying, importing sequential datasets from mainframes, and parallel data transfer. Sqoop facilitates bi-directional data transfer between Hadoop and relational databases.
Oozie -
Oozie is a workflow scheduling system designed for managing Apache Hadoop jobs. It combines multiple jobs sequentially into one logical unit of work (UOW). For Apache jobs, Oozie functions similarly to a scheduler.
Oozie is very flexible, allowing users to easily start, stop, suspend, and rerun jobs. It also provides if-then-else branching and control within Hadoop jobs.
There are two kinds of Oozie jobs -
- Oozie Workflow – Oozie workflows are used to store and run collections of Hadoop jobs, such as MapReduce, Pig, and Hive.
- Oozie Coordinator – Coordinators run workflow jobs based on predefined schedules and the availability of data.
HBase -
HBase is an open-source, scalable, distributed, non-relational database known as a NoSQL database, built on top of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). It supports all types of data, including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. HBase can be accessed through a Java API, and it also provides ODBC and JDBC drivers.
There are two main components of HBase: the HBase Master and the Region Server. The HBase Master is responsible for load balancing across all Region Servers, although it does not actually store data itself. The Region Server, on the other hand, acts as the worker node that handles read, write, update, and delete requests from clients.
Flume -
Flume efficiently collects, aggregates, and moves large amounts of data from its origin to HDFS. With Flume, data can be transferred immediately from multiple servers to Hadoop. Additionally, it supports the transfer of online streaming data from various sources, such as network traffic, social media, email messages, and log files, into HDFS. Flume acts as a real-time loader for streaming data into Hadoop.
Mahout -
Mahout is well-known for its capabilities in machine learning. It is an open-source framework designed for creating scalable machine learning algorithms and a data mining library. Machine learning algorithms enable the development of self-learning machines that can evolve independently, without being explicitly programmed.
Mahout provides data science tools that automatically identify meaningful patterns in data stored in HDFS big data sets. The main algorithms offered by Mahout include:
- Classification - It learns from existing categories and assigns unclassified items to the most appropriate category.
- Clustering - It organizes items within a specific class into naturally occurring groups.
- Collaborative filtering - It analyzes user behavior to make personalized product recommendations.
- Frequent itemset missing - It examines which items are likely to appear together in datasets.
Yarn -
YARN stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator. Apache YARN is a component of Hadoop, but it can also function as a standalone resource manager.
YARN is responsible for providing the computational resources required for application execution. It comprises two key elements: the Resource Manager and the Node Manager.
The Resource Scheduler determines how to allocate resources, working in conjunction with the Scheduler and Applications Manager. The Node Manager receives instructions from the YARN Scheduler to decide which node should execute which task.
HCatalog -
HCatalog is a management layer for storage and tables within Hadoop. It allows different data processing tools, such as Pig and MapReduce, to be utilized by users. With HCatalog, users can easily read and write data in the Hadoop grid without needing to redefine input schemas.
The HCatalog table concept provides a relational view of data stored in the HDFS. It can display data in a tabular format from various file types, including RCFile, text files, and sequence files. Additionally, HCatalog offers APIs that enable external systems to access the metadata of these tables.
Spark -
Apache Spark is both a programming model and a computing framework designed for real-time data analytics in a distributed computing environment. It performs in-memory computations, which significantly increases the speed of data processing compared to MapReduce, a key reason for its popularity.
Spark workloads typically run between 10 and 100 times faster than those that rely on disk execution. Additionally, Spark can be used independently of Hadoop and supports SQL, addressing some limitations of core Hadoop technology. The Spark programming environment is compatible with Scala, Python, and R, allowing for interactive use.
Apache Drill -
Apache Drill is a low-latency, distributed query engine designed for processing large-scale data, including both structured and semi-structured data. It is capable of scaling to thousands of nodes and can query petabytes of data effectively.
As an open-source application, Drill integrates well with Hive, allowing developers to leverage their existing Hive deployments. The primary strength of Apache Drill lies in its ability to combine data from various data stores using a single query.
Ambari -
Ambari is a management platform designed for provisioning, managing, monitoring, and securing Apache Hadoop clusters. It supports various components of the Hadoop ecosystem, including HDFS, MapReduce, Hive, HCatalog, HBase, Zookeeper, Oozie, Pig, and Sqoop.
Ambari provides a consistent and secure platform for operational control, featuring simplified installation, configuration, and management. It offers a centralized security setup, is highly extensible and customizable, and provides full visibility into the health of the cluster.
Zookeeper -
Apache Zookeeper is a centralized service that helps maintain configuration information, manage naming, provide distributed synchronization, and offer group services.
Zookeeper saves considerable time by handling synchronization, configuration maintenance, grouping, and naming efficiently. It performs well in scenarios where reading data is more common than writing data. Additionally, Zookeeper keeps a record of all transactions.
